Brief introduction of cadmium telluride thin film solar cell

10cm*10cm small cadmium telluride thin film solar cell module cadmium telluride thin film solar cell is abbreviated as CdTe battery, which is a thin film solar cell based on heterojunction of p-type CdTe and n-type Cd.
The first cadmium telluride thin film solar cell was fabricated by an RCA laboratory alloyed with In on a CdTe single crystal, and its photoelectric conversion efficiency was 2.1%. In 1982, Kodak Laboratories used a chemical deposition method to prepare an ultra-thin CdS on P-type CdTe to prepare a heterojunction p-CdTe/n-CdS thin film solar cell with an efficiency of more than 10%. This is the prototype of the current stage of cadmium telluride thin film solar cells. In the early 1990s, cadmium telluride thin film solar cells have achieved large-scale production, but the market is developing slowly, and the market share has been hovering around 1%. At present, the highest photoelectric conversion efficiency obtained by cadmium telluride thin film solar cells in the laboratory has reached 17.3% [1]. The conversion efficiency of its commercial modules has also reached about 10%.
Advantages of cadmium telluride thin film solar cells
Ideal forbidden band width
The forbidden band width of CdTe is generally 1.45 eV, and the spectral response of CdTe matches the solar spectrum very well.
High light absorption rate
The absorption coefficient of CdTe is as high as 104 cm-1 or more in the visible light range, and 95% of photons can be absorbed in the absorption layer of 1 μm thick.
High conversion efficiency
The theoretical photoelectric conversion efficiency of cadmium telluride thin film solar cells is about 28%.
Stable battery performance
The general cadmium telluride thin film solar cell is designed to be used for 20 years.
Simple battery structure
Low manufacturing costs and easy to achieve large-scale production.
Structure of cadmium telluride thin film solar cell
A cadmium telluride thin film solar cell is a photovoltaic device formed by sequentially depositing a multilayer film on a glass or other flexible substrate. The general standard cadmium telluride thin film solar cell consists of a five-layer structure:
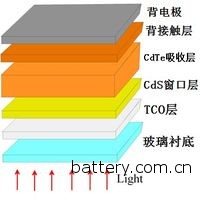
Schematic diagram of cadmium telluride thin film solar cell structure
Mainly for the battery to support, prevent pollution and incident sunlight.
TCO layer
That is, a transparent conductive oxide layer. The main function is the function of light transmission and conduction.
CdS window layer
An n-type semiconductor, which forms a pn junction with p-type CdTe.
CdTe absorption layer
It is the main light absorbing layer of the battery, and the pn junction formed with the n-type CdS window layer is the core part of the entire battery.
Back contact layer and back electrode
In order to lower the contact barrier of the CdTe and the metal electrode, a current is drawn to make the metal electrode form an ohmic contact with the CdTe.
Method for preparing cadmium telluride thin film solar cell
It can be prepared by a variety of methods such as chemical water bath deposition (CBD), near space sublimation, screen printing, sputtering, evaporation, and the like. The general industrialization and laboratory use the CBD method because the cost of the CBD method is low and the generated CdS can form a good and intimate contact with the TCO.
Blow Molding Heat shrinkable film Packaging usage
CANGZHOU XINFENG PLASTIC CO.,LTD , https://www.xinfengplastics.com